

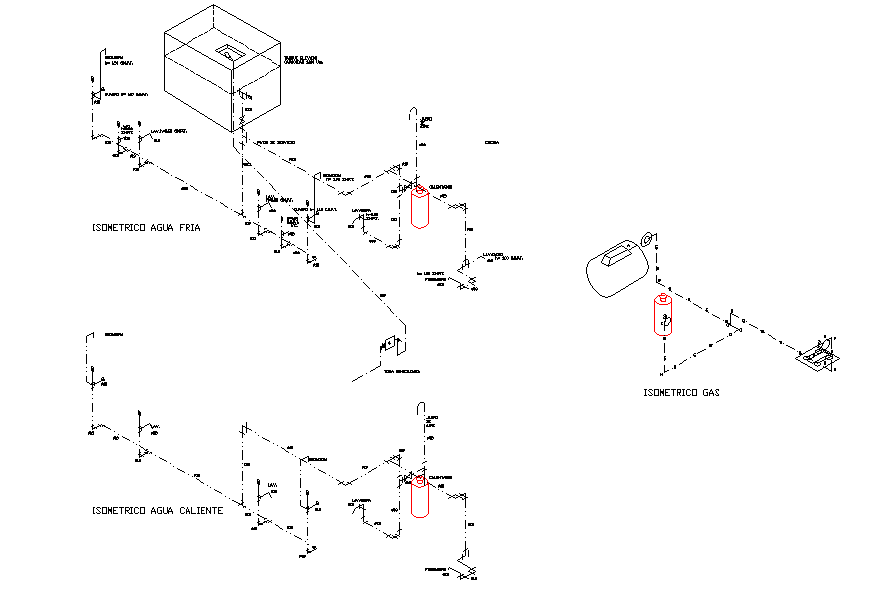
As a result, valves and chokes provide isolation and metering on headers to satisfy the needs of the application. The flow rate value highly depends on the supply pressure and line sizes, and thus requires proper consideration. Also, in drainage applications, professionals set a threshold flow rate to avoid hold up at drains. To satisfy the production requirements in a facility, flow rates for each line must meet a set value or within a limit. All these elements require consideration when designing a header. In addition, there are pressure drops due to the presence of bends and tees on the header. The use of chokes and valve help mitigate this risk. Without proper design, a high-pressure branch could cause backflow into a lower pressure branch. On the other hand, for a collecting header, different sources flowing into a single header at diverse pressures also pose a challenge. As a result, engines can deliver measurably better horsepower, torque, and mileage. Moreover, their presence is necessary especially when aggregating fumes from multiple combustion chambers.

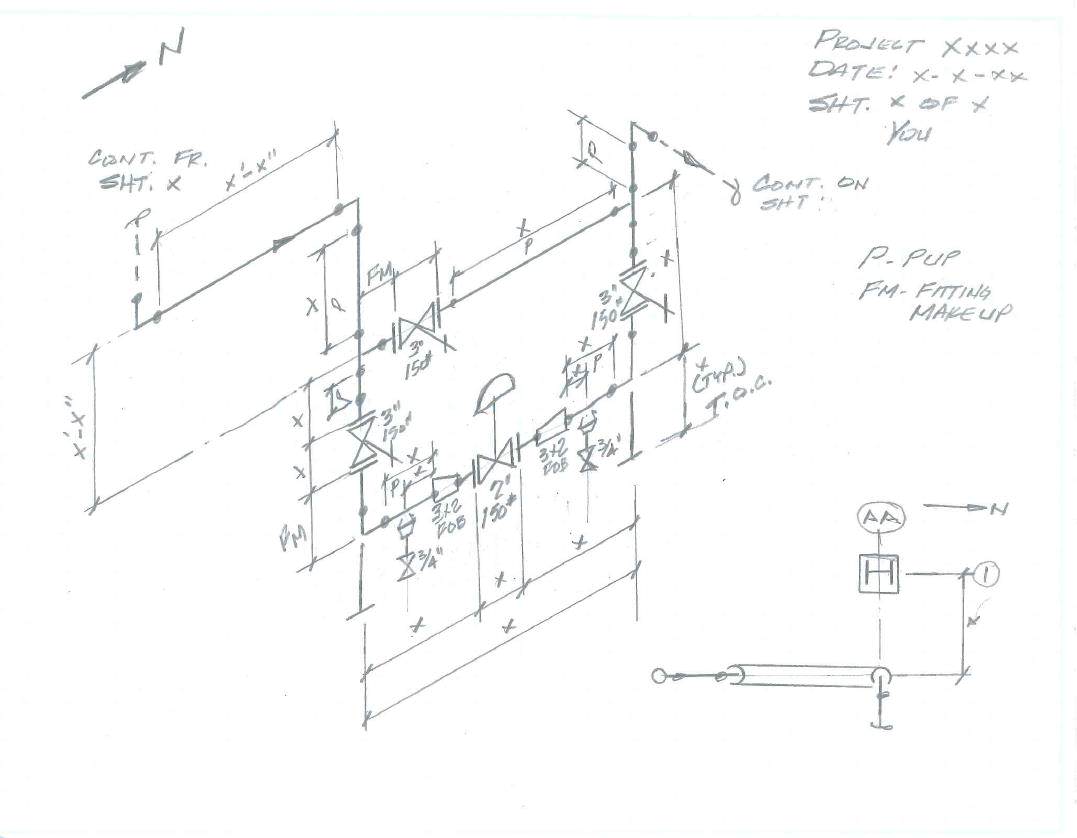
On the other hand, it can also distribute flow to many smaller pipes (distributing header). Pipeline Header PurposeĪ pipeline header refers to a large pipe that is set up to aggregate flow from smaller pipes (collecting header). In this article, you will learn the purpose of a pipeline header, important factors in its design, and calculation methodology. A pipeline header connects flowlines from several different sources into a single gathering line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
